Difference between revisions of "SHN FAQ"
(Created page with "===What VoIP protocols and voice transmission formats do Synway VoIP boards support?=== Protocol: SIP; Voice transmission formats: G.711 A-law, G.711 μ-law, G.729A, GSM. ==...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 11:31, 12 May 2015
Contents
- 1 What VoIP protocols and voice transmission formats do Synway VoIP boards support?
- 2 Which part of SIP protocol is supported by Synway VoIP boards at present?
- 3 Do VoIP boards support conferencing?
- 4 Do VoIP boards support the access to IMS devices?
- 5 Why are there a lot of echoes on the line when making an IP call?
- 6 The IP board driver is loaded successfully but the channel state shows unusable. Why?
- 7 Which purposes can VoIP boards be used for?
- 8 What methods do Synway VoIP boards support for DTMF transmission? What is the difference among them?
- 9 What contributes to failure of initializing VoIP boards?
- 10 What causes call failure on IP channels?
- 11 What is the SIP log for? How to set its levels?
- 12 What may contribute to failure of using VoIP boards for registration?
- 13 When a B-type VoIP board is configured with proper registration information to register a server on the public network, the channel state shows registration failed while the application is running, why? How to locate the exact reasons?
- 14 What do you do if the DTMF digits received by SHN series boards fail to be passed over bus to the cooperating SHD/SHT series boards and consequently fail to be sent out by them?
- 15 How to deal with such voice problems as poor voice effect, no voice pass, single voice pass, noise, etc, appearing in normal calls on a VoIP board?
What VoIP protocols and voice transmission formats do Synway VoIP boards support?
Protocol: SIP;
Voice transmission formats: G.711 A-law, G.711 μ-law, G.729A, GSM.
Which part of SIP protocol is supported by Synway VoIP boards at present?
RFC3261.
Do VoIP boards support conferencing?
Yes. They include H.100 bus interface to enable conferencing with other boards.
Do VoIP boards support the access to IMS devices?
Currently, the VoIP boards support the connection to the CMCC IMS network.
Why are there a lot of echoes on the line when making an IP call?
This can happen if there is network delay or echo cancellation at the remote end is poor.
The IP board driver is loaded successfully but the channel state shows unusable. Why?
Usually, this can be resolved by doing the following steps and settling relative problems.
1) Check if the VoIP board is well connected to network. If the network connection fails, the channel state will transfer to “Unusable”.
2) Examine if the IP setting in the configuration program matches the actual IP address of the local PC.
3) See if communication ports are occupied by other application programs.
Note: For SynCTI Ver. 5.3.2.1 and above versions, if case 2) or 3) occurs, the board will fail to be initialized and the system will report error. Therefore, the channel state will not transfer to “Unusable”.
Which purposes can VoIP boards be used for?
The VoIP boards can be used with other voice boards from Synway to help develop multiple VoIP platform systems, such as trunking gateway, VoIP call center and IP PBX.
What methods do Synway VoIP boards support for DTMF transmission? What is the difference among them?
The SIP protocol supports in-band, RFC2833 and SIP Info to send DTMF.
The SIP protocol stacks adapted for the VoIP board use the RTP data packets to transmit voice data,
The RTP data packet consists of two parts: RTP header and RTP payload.
RFC2833: The RTP header carries DTMF information. This method provides high discrimination but may cause data loss in poor networks as the RTP data packet is delivered on the basis of UDP.
In-band: The RTP payload carries DTMF information. Because the information is encoded and needs to be decoded in hardware, this method provides a lower discrimination than RFC2833, and also it may cause data loss in poor networks.
SIP Info: The SIP message carries DTMF information. This method provides high discrimination but may cause data loss in poor networks as the SIP signaling packet is delivered on the basis of UDP.
What contributes to failure of initializing VoIP boards?
Reasons for failure to initialize VoIP boards based on SIP protocol:
- Signaling IP or signaling port set incorrect
When an improperly configured signaling IP or signaling port is occupied by other application programs, the initialization of the VoIP board will fail.
- Network card connected with no network or connection invalid
If the signaling IP is not a loop address and the corresponding network card connects with no networks or the connection goes invalid, the initialization of the VoIP board will fail.
What causes call failure on IP channels?
Reasons for call failure on IP channels:
- Incorrect target address or port
Check the setting of IP address and port at the remote end. The default signaling port suggested by SIP protocol is 5060.
- A party of the call is behind firewall or NAT
If a party of the call stays is behind NAT, it is necessary to perform NAT traversal with the help of IP server; if a party or both parties of the call stay behind firewall, it is necessary to check if the call has been blocked by the firewall.
- Signaling messages incompatible
The call probably fails because incompatibility of signaling messages occurs during the call. Use capture software like wireshark to check if there is something wrong with signaling connection.
- Others
Other reasons, such as network faults and IP server breakdown, can also cause call failure on IP channels. Use capture software like wireshark to check.
What is the SIP log for? How to set its levels?
The SIP log is an effective tool for positioning errors. The output logs are usually used to analyze:
- why the call cannot be established;
- why the sound cannot be heard or the sound effect is bad;
- the previous situation of the current call state machine and how it processes call aberrance;
- the pressure of the current call;
- whether the A3 event has been thrown out properly.
We suggest you set the log level to Error while operating a program, set it to INFO1 while debugging a program, and set it to INFO2 when errors occur in a program.
What may contribute to failure of using VoIP boards for registration?
This is probably because the registration port of the VoIP board or the registration server is occupied.
When a B-type VoIP board is configured with proper registration information to register a server on the public network, the channel state shows registration failed while the application is running, why? How to locate the exact reasons?
1) Problems in board or driver
To confirm that there is nothing wrong with the board and the driver, first you should apply the default setting of the board and start the test program to check if all channels stay in the idle state. Then select Channel 0 to call the default IP address, fill in the DTMF column with 192.168.1.1 (i.e. the local PC) and invoke the function SsmAutodial. If Channel 1 rings, it means the board self-loop configuration is passed, both call and talk going well within the loop.
2) Registered account or SIP server unavailable
Install an SIP soft-terminal and use the registered account to see if you can register the server and call out successfully. If you can, it is sure that there is nothing wrong with the registered account and SIP server too.
3) The SIP server doesn’t pass the authentication information sent from the board.
4) Certain SIP servers only support a particular model of soft-terminals or IP phones.
What do you do if the DTMF digits received by SHN series boards fail to be passed over bus to the cooperating SHD/SHT series boards and consequently fail to be sent out by them?
DTMF digits can be transmitted over IP by the following three methods.
- In-band Mode: delivering DTMF by voice;
- Out-of-band Mode: delivering DTMF by signaling;
- RFC2833 Mode: RFC2833 is the standards-based mechanism used to send DTMF digits in-band (RTP). In this mode, the DTMF signals are packed to be different from common voice data before being sent or received.
If you don’t use the in-band mode to send DTMF digits, the problem as described in the question will probably occur. There are two ways to solve this problem. See below.
1)Modify the DTMF transmission mode for the IP device that communicates to the SHN series board. Change it to in-band mode. Then the DTMF signals will be delivered by voice and passed over bus directly to the SHD/SHT series board, and sent out straight by the SHD/SHT series board.
2)Use the program flow control solution. First, use the SHN series board to receive the DTMF signals that are sent in out-of-band or RFC2833 mode. Then invoke the function SsmTxDTMF on the corresponding channel of the SHD/SHT board that is connected with the SHN board by bus, to pass the DTMF digits and subsequently send them out.
How to deal with such voice problems as poor voice effect, no voice pass, single voice pass, noise, etc, appearing in normal calls on a VoIP board?
During the process a Synway VoIP board starts and establishes a call with other VoIP terminals, voice data and signaling messages are transmitted respectively. The former is over RTP protocol while the latter is over SIP protocol.
If the Synway VoIP board is able to connect a call with other IP terminals, it indicates the signaling interact between both parties is good. To find the reasons and solutions for no-voice-pass failure, refer to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th of the below; to find the reasons and solutions for poor voice effect, refer to the 6th of the below; to find the reasons and solutions for poor speech quality, refer to the 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th of the below; to find the reasons and solutions for single-voice-pass problem, refer to the 3rd, 4th and 5th of the below.
See below for details.
1) If the IP address for voice transmission is unusable, the no-voice-pass failure may appear. Causes and troubleshootings are as follows:
a) The board is not connected to a network cable or the modular plug is loose. You can go in the operating system ‘StartàRun’ and use the ‘ping’ command to check.
b) There is ARP virus (address deceiving virus) in the network. As to the method of detecting whether your computer has been infected by this kind of virus, you can search it on the Internet.
c) If the board is connected via a network cable to a network exchange on which the IP address assigned to the board is bound to other MAC address, it may cause the no-voice-pass failure. You can check the configurations of the network exchange to exclude this possibility.
2) The UMCT series IP board has a front panel and a rear panel. The network interface is located on the rear panel. So if the front and rear panels are not in position, it will lead to the no-voice-pass failure.
3) If one or both parties of a call have installed a firewall or the like, it may cause voice streams being blocked and lead to the no-pass or single-pass problem. Now you can use a capture software like wireshark to verify the reception of RTP voice streams.
Note: The RTP voice data packet of a B-type VoIP board transmits over the network interface. For how to capture the RTP packet, please feel free to contact our technicians.
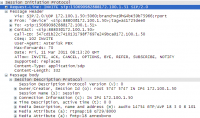
4) If one or both parties of the call stay behind NAT, the poor capability in NAT traversal of either party may cause the single-pass problem or even the call failure. Now you can use a capture software like wireshark to capture signaling packets for analysis and check whether the following 2 IP addresses are public network addresses. The field Contact gives the signaling IP address while the field Connection Information gives the IP address to transmit the RTP data.
5) If a VoIP board seats in a LAN and an incoming party telnets to the LAN via a remote tool and establishes a call with the VoIP board, the field SDP in the Invite message which is sent by the incoming party indicates the IP address of the public network, and the VoIP board will reply by the IP in SDP but not by the original IP in the RTP packet, which will cause the single-pass problem and make the other party not hear from the VoIP board. To solve this problem, you can modify the configuration item AutoDetectRemoteRTPAddress to enable the remote RTP address self-adaptive feature.
6) The quality of network has a significant effect on the voice. If the voice effect is not satisfactory, you may use the following ways to adjust it:
a) Broaden the network bandwidth. A too-narrow bandwidth may result in the network congestion as well as a longer delay in data transmission.
b) Use G.729 codec. G.729 corresponds to the rate of 8kbps while G.711 A-law and G.711 μ-law correspond to the rate of 64kbps. Using G.729 can greatly reduce the bandwidth for a voice path. Actually, when the SHN-32A-CT/PCI board uses G.711 A-law or G.711 μ-law, the bandwidth for a voice path is 78.4kbps; when it uses G. 729, the bandwidth for a voice path is only 22.4kbps.
7) The mismatch of the voice CODECs between RTP packets on both sides results in the appearance of noise. In such situation, you can use a capture software to record the RTP data at both parties during the call and analyse the coding format to verify or eliminate this cause.
8) The inconsistency of the load of RTP packets on both sides may result in the appearance of noise. At present, our driver supports the load of 20ms or 30ms, which can be configured via the configuration items SizeG711A, SizeG711U and SizeG729.
9) In a system there is another board (for example SHD series board) besides the VoIP board and these two boards are connected with each other by CT-BUS, if the other board is uninitialized, noise may appear during the call on the VoIP board. So in case the other board is not used, you‘d better disconnect it from the VoIP board.
10) If it is the soft terminal that is talking to the VoIP board, the following two reasons may cause such voice issues:
a) As the called party, sometimes eyebeam1.1 can not hear from the calling party because of the incompatibility with Win7. Update to eyebeam1.5 to fix this problem.
b) The improper configuration of the sound card at the soft terminal may result in the appearance of noise, current noise, echo, etc. To fix it, modify the configuration of the sound card in the corresponding operating system.
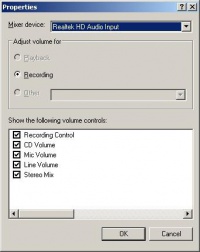
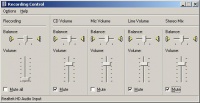
In WinXP: At the lower right corner of your desktop, click to choose ‘Volume’ > ‘Options’ > ‘Properties’ > ‘Mixer device’ > ‘Recording’, go ‘Recording Control’ and set ‘CD Volume’, ‘Line Volume’, ‘Stereo Mix’ to Mute. See below:
In Windows 2003: At the lower right corner of your desktop, click to choose ‘Volume’ > ‘Properties’ > ‘Recording’, go ‘Recording Control’ and set ‘CD Volume’, ‘Line Volume’, ‘Stereo Mix’ to Mute.
In Win7: Go to ‘Recording Control’ > ‘Microphone’, and set ‘MIC Boost’ to 0.
If all the possibilities mentioned above have been excluded, the cause may lie in the physical fault of the board. You can contact our customer service to replace the board for further tests.