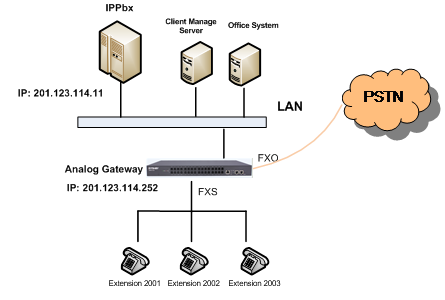
General Application of Analog Gateway – IVR
The following operations are supported:
- PSTN can make calls to FXO, and then dial extensions at FXS according to the prompt tone.
- Each extension at FXS can call PSTN via FXO.
- Extensions at FXS can call each other.
To attain these purposes, take the following steps to configure the gateway.
1) Do SIP settings.
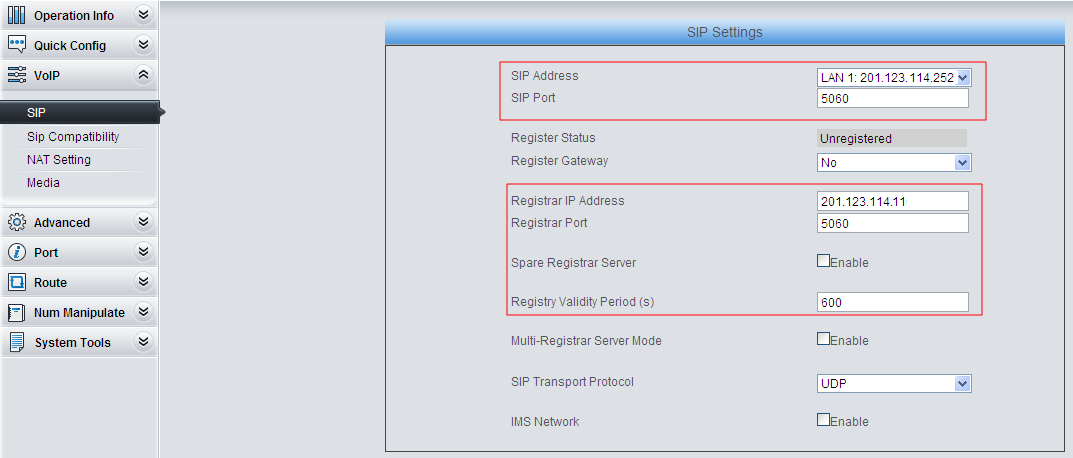
Set the LAN for SIP call processing and the IPPBX (with sip server function) address.
2) Do FXO settings.
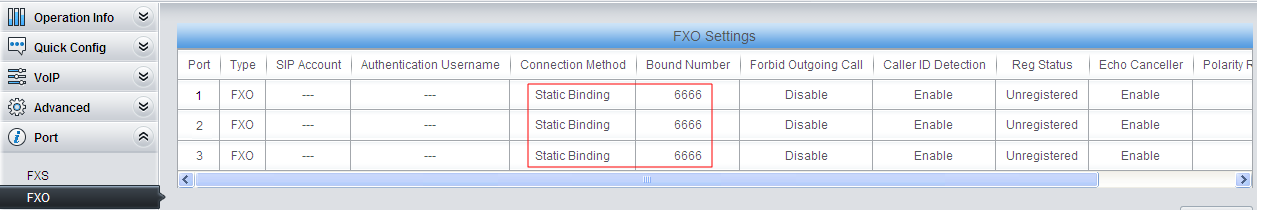
Set the properties of each FXO port. The item Connection Method can be set to Static Binding with the bound number of 6666 which is determined by IPPBX. That is, once receiving the call with 6666 as its username from the called party, IPPBX will go into the PBX service flow. The effect of the analog gateway here is just to switch calls from PSTN to the IPPBX service layer.
3) Do FXS settings.
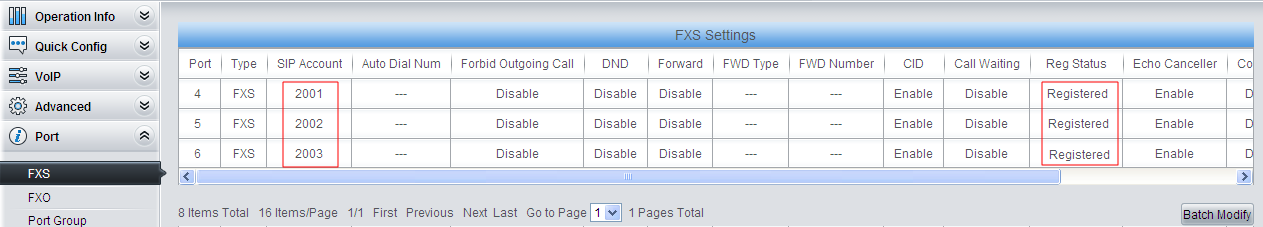
Set a SIP account for each FXS port, which will be used in registration to IPPBX. On request of speaking to the phone operator or switching the call to an extension, IPPBX will follow the service flow to switch the call to the extension with the corresponding SIP account or to the phone operator.
4) Do port group settings.
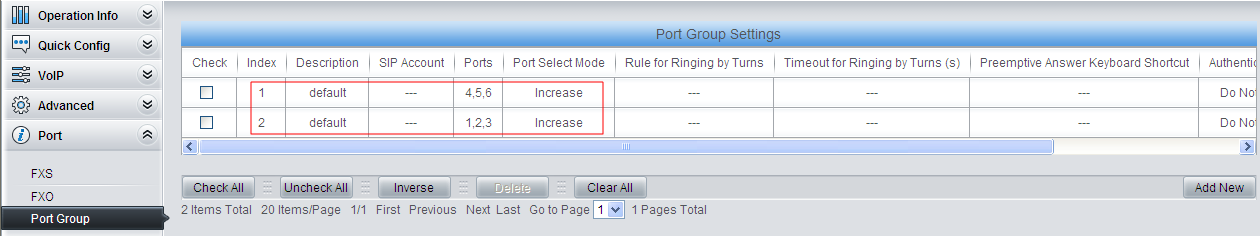
Add three FXS ports with indexes 4, 5 and 6 to Port Group 1, and three FXO ports with indexes 1, 2 and 3 to Port Group 2, preparing for subsequent route settings.
5) Set TEL –> IP routing.
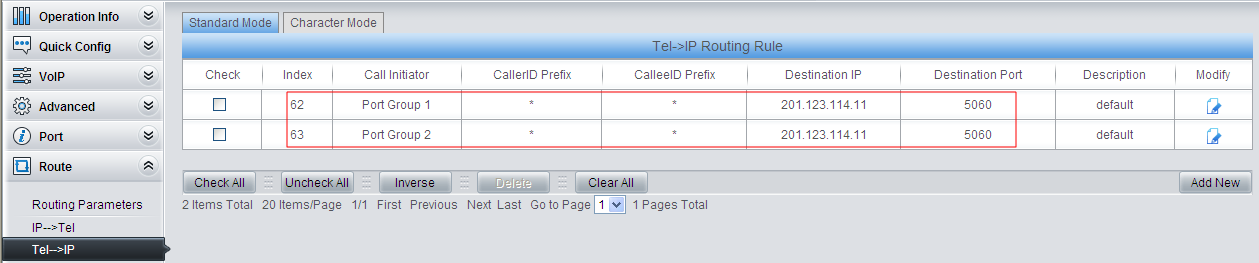
Set to switch the FXS (Port Group 1) and FXO (Port Group 2) calls to IPPBX.
6) Set IP –> TEL routing.
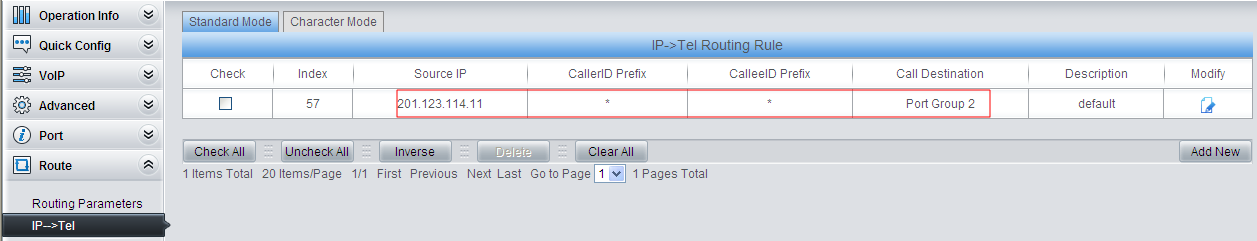
Add an IP –> TEL routing and set all IP calls from IPPBX to go out via FXO (Port Group 2). Settings related to the outgoing call number are processed by IPPBX.
The IVR system with IPPBX as described above is mainly used in some complex environments. However, a simple requirement can be achieved by an IVR system with the analog gateway only where IPPBX is not necessary.
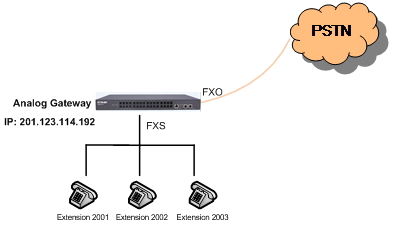
The scenario without IPPBX also supports the following operations.
- PSTN can make calls to FXO, and then dial extensions at FXS according to the prompt tone.
- Each extension at FXS can call PSTN via FXO.
- Extensions at FXS can call each other.
Follow the steps below to set the analog gateway.
1) Do SIP settings.
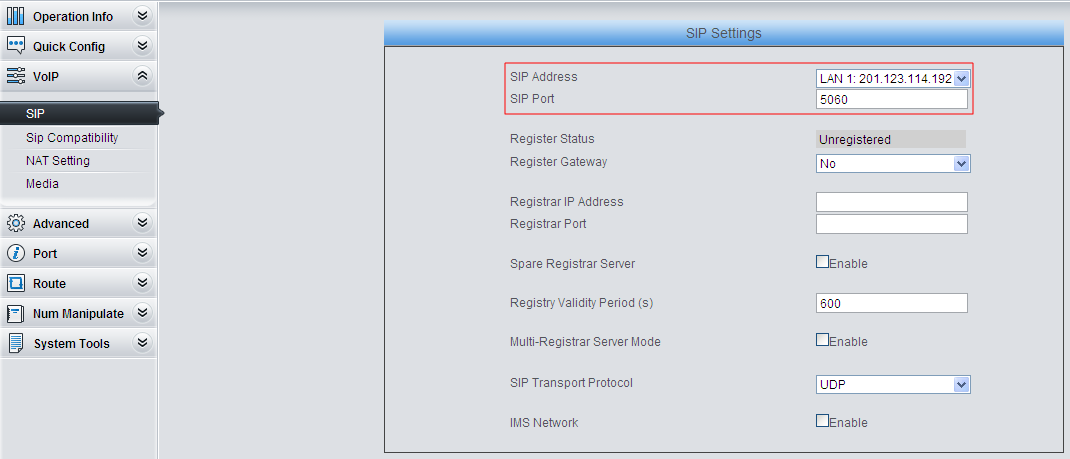
Set the LAN for SIP call processing.
2) Do FXO settings.
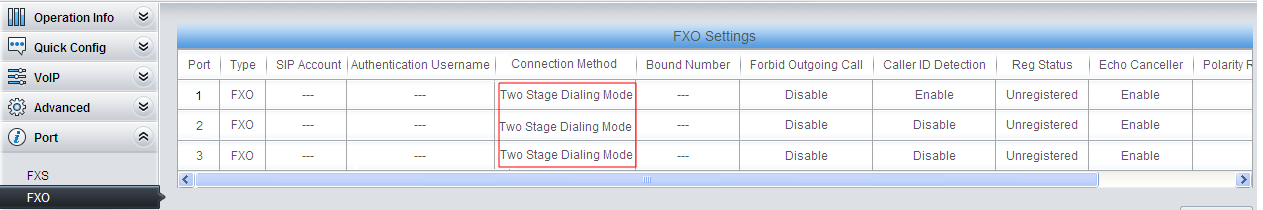
Set the connection method to ‘Two Stages Dialing Mode’. Once there is a call coming from FXO, the gateway will play the prompt tone ‘Please dial the extension number’. Then the gateway will switch the call to the extension with the corresponding extension number.
3) Do FXS settings.
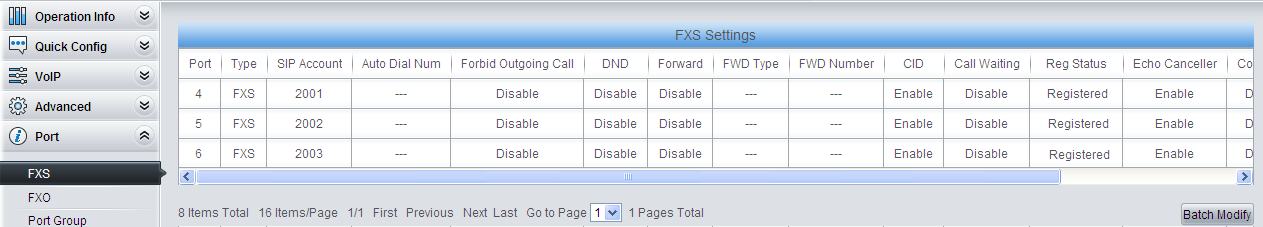
Set the SIP account of each FXS port, i.e. the extension number of each FXS port.
4) Do port group settings.
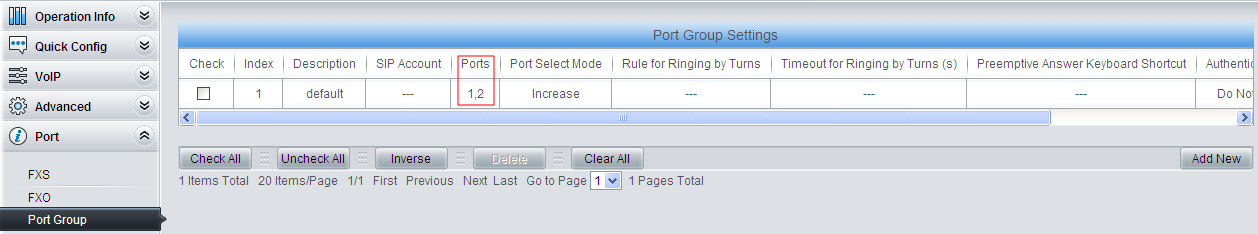
Add FXO ports to Port Group 1, preparing for subsequent route settings.
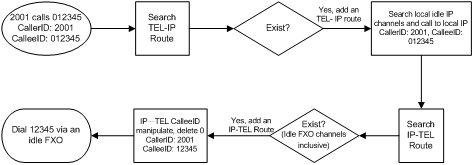
5) Set TEL –> IP routing.
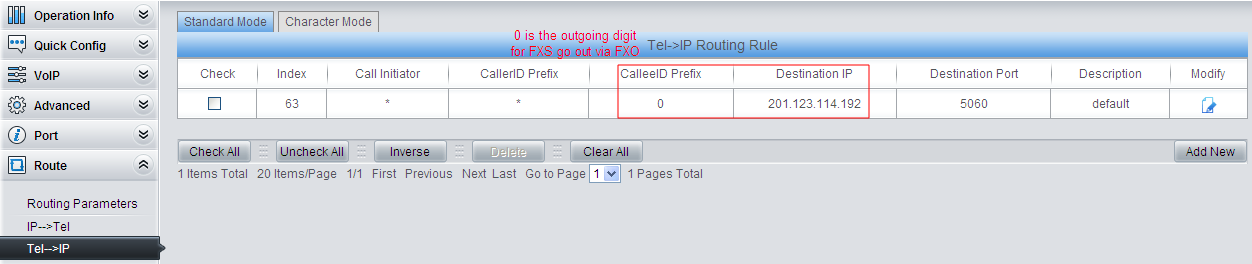
Set the outgoing digit and route used for FXS to dial out via FXO. As there is a default route--- ‘Route by Number’ on the gateway, it is unnecessary to add another route for calling from extension to extension. However, for an FXS call dialed out with a prefix 0, as there is no SIP account starting with 0, the route should be set as shown in the figure above. Thus, the call can find a corresponding route to dial out.
6) Set IP –> TEL routing.
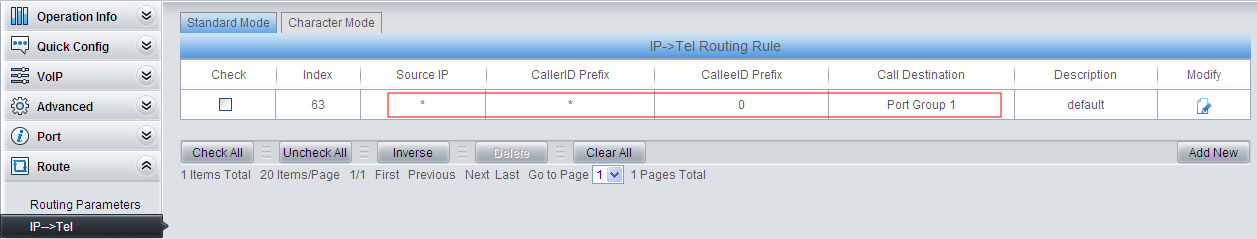
Configure that if the called party number starts with 0, the call will go out via FXO (Port Group 1). Here 0 is the outgoing digit. Step 5 and step 6 are only used for FXS to dial out via FXO.
7) Two modes ‘Two Stages Dialing Mode’ and ‘Dialing directly’ are available for the dialing of FXO port
With the connection method set to ‘Two Stages Dialing Mode’, the gateway configuration finishes after you complete the following setting. Under this mode, a call initiated by FXS with the outgoing number set to 0 will not be switched to FXO until you wait for 6 seconds (as 0 doesn’t exist in the dialing rule) or press # after dialing 0 at FXS.
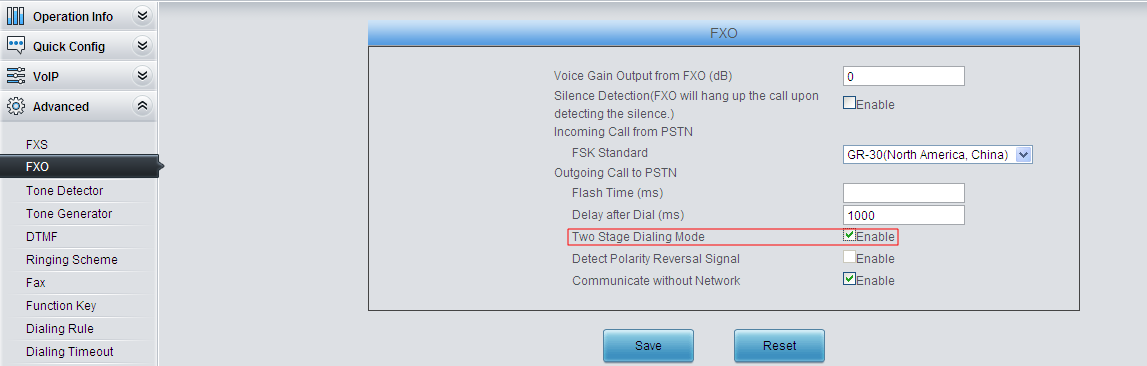
If you’d like to dial out from FXO directly, it is required to set IPTel CalleeID manipulation as follow. Thus, the first digit 0 of the number will be removed before the number is dialed out through FXO.
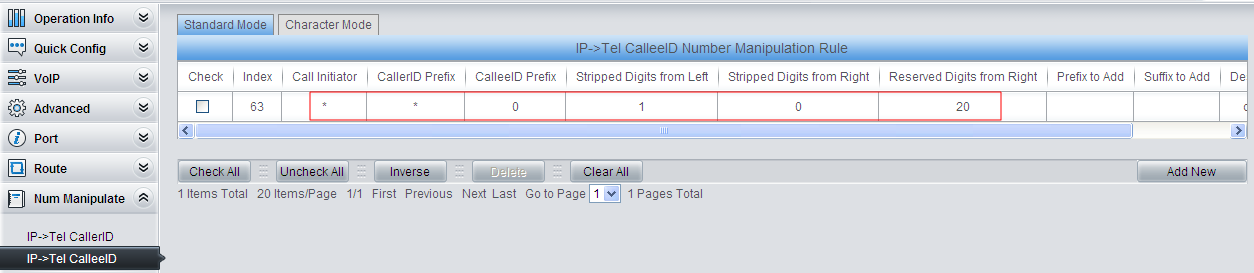
This number manipulation process is illustrated in the diagram below.